Dr AvinashTank, is a super-specialist (MCh) Laparoscopic Gastro-intestinal Surgeon,



Frequently Asked Questions
- All
- OBESITY (Bariatric) SURGERY
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Cancer Surgery
- Gastro Intestinal Surgery
- PANCREAS SURGERY
- Home Page
- DIABETES SURGERY
- Endoscopy
- Medical Tourism
There are 9 organs are involved in process of food digestion, once your enjoy tasty food. If all organs are listed as per their specific name, then there are 17 organs are working together.
Our food digestion starts from mouth (oral cavity) where digestion begins. It is responsible for chewing and breaking down food into smaller pieces. The diseases of this area is taken care by dentist. So for care point of view, digestive organ starts from Esophagus (Food Pipe)
- Esophagus:
- A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. It transports food from the mouth to the stomach through rhythmic contractions called peristalsis.
- Stomach:
- A muscular organ that receives food from the esophagus. It secretes gastric juices that help break down food and mix it into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
- Small Intestine:
- This is the longest part of the digestive tract and consists of three segments: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
- The small intestine is responsible for the absorption of nutrients from food into the bloodstream.
- Liver:
- The largest internal organ, located in the upper right portion of the abdomen.
- It produces bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats, and performs various metabolic functions.
- Gallbladder:
- A small organ located beneath the liver.
- It stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver, releasing it into the small intestine when needed for digestion.
- Pancreas:
- A glandular organ situated behind the stomach.
- It produces digestive enzymes that are released into the small intestine to further break down food, as well as insulin and other hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
- Large Intestine (Colon):
- This organ absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining digested material, forming feces.
- The colon also houses beneficial bacteria that aid in the breakdown of undigested food and the production of certain vitamins.
- Colon is about 150 cm long and its identified by different name: Caecum, Ascending Colon, Hepatic Flexure, Transverse Colon, Splenic Flexure, Descending Colon, & Sigmoid Colon.
- Rectum:
- The final portion of the large intestine where feces are stored until they are eliminated from the body.
- Anus:
- The opening at the end of the digestive tract through which waste material is expelled from the body.
These organs work together to facilitate the digestion and absorption of nutrients from food and eliminate waste products from the body.
Appendix: The appendix is not an organ of active food digestion in humans. It’s a rudimentary organ. Its located at the junction of the small intestine and large intestine. The diseases of the appendix are treated by a gastro-surgeon.
Preventing diseases of the digestive organs involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and following good preventive practices. Here are some general guidelines to help prevent diseases of the digestive system:
- Eat a healthy diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-fat foods. Adequate fiber intake can help maintain bowel regularity and reduce the risk of conditions such as constipation and diverticulosis.
- Stay hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to support proper digestion and maintain optimal bowel function. Aim for at least eight cups of water daily, or more if needed.
- Practice portion control: Avoid overeating and practice portion control to maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight can increase the risk of conditions such as acid reflux, gallstones, and fatty liver disease.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Aim to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Obesity is associated with an increased risk of conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gallbladder disease, and certain cancers.
- Be physically active: Engage in regular physical activity such as walking, jogging, cycling, or any exercise that you enjoy. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, improves digestion, and reduces the risk of certain digestive disorders.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver disease, pancreatitis, and other digestive disorders. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. The recommended limits are up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Avoid tobacco use: Smoking increases the risk of various digestive conditions, including peptic ulcers, Crohn’s disease, colorectal cancer, and pancreatic cancer. Quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke
- Practice safe food hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly before handling and consuming food. Ensure that your food is properly cooked, stored, and handled to prevent foodborne illnesses that can affect the digestive system.
- Get vaccinated: Follow the recommended vaccination schedules to protect against hepatitis A and B, which can cause liver inflammation and other digestive complications.
- Schedule regular check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider for regular check-ups and screenings. Early detection and timely treatment of digestive disorders can significantly improve outcomes
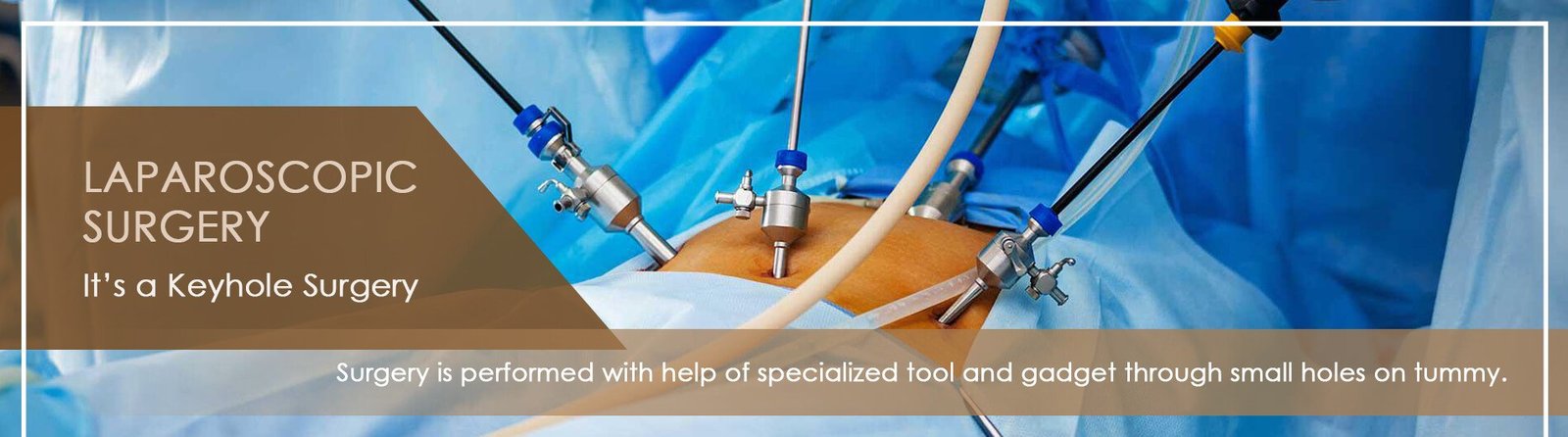
The laparoscopy approach is used to see the outer side of digestive organs. Laparoscopy is used to make a diagnosis of a few diseases and is mainly used for the treatment of almost all diseases of digestive organs.
Laparoscopy is a surgical technique that involves making small incisions in the abdomen to access and operate on internal organs. It utilizes a laparoscope, which is a thin, long tube equipped with a light source and a camera.
The benefits of laparoscopy compared to traditional open surgery include smaller incisions, reduced scarring, less pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and a lower risk of complications.
Laparoscopic surgery is commonly used in various surgical procedures, including gallbladder removal, appendectomy, hernia repair, colorectal surgery, cancer surgery and bariatric surgery.
Endoscopy is a procedure to see the inner side of the digestive tract using a flexible tube with a camera called an endoscope.
It helps in the diagnosis and treatment of various gastrointestinal conditions by allowing direct visualization and the collection of tissue samples for biopsy.
Gastroenterologists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), liver diseases (such as hepatitis and cirrhosis), gallbladder and biliary tract disorders, pancreatic disorders, and gastrointestinal cancers.
Treatment by Medicines: There are few diseases which are primarily treated by medicines, like
- Simple gas or acidity
- Jaundice due to Liver infection (Hepatitis A,B,C,D,E)
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Diarrhea due to infection of intestine
Treatment by Surgery: There are few diseases which are primarily treated by surgery, like
- Gallbladder Stone, Pancrease Stone, Liver Stones
- Hernia (Umbilical, Incisional, Hiatus, Inguinal, Femora)
- Appendix
- Intestinal Blockage, Intestinal Bleeding, Intestinal Perforation
- Cancer of all digestive organs
- Bariatric Surgery
Treatment by Medicines (First) & by Surgery (Later On):
There are few diseases, which are initially treated by medicines. If these diseases do not completely improve, recur after initial treatment or when the patient develops side effects of drugs required for the long term, surgery is offered as last and more effective treatment for such diseases. Like
- Acidity or Reflux or GERD due to weak valve or associated hiatus hernia
- IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Ulcerative Colitis, Crohn’s Disease)
- Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Liver Cirrhosis with complications
You should consider seeing a gastroenterologist / Gastro surgeon if you experience problems with persistent or recurring symptoms related to your digestive system, such as
- Abdominal pain
- Vomit
- Blood Vomit
- Jaundice
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Gas
- Heartburn (Acidity / Reflux / GERD)
- Swallowing difficulties
- Rectal bleeding
- Unexplained weight loss.
Most people misunderstand that gastro doctors only treat problems related to gas in the tummy. Along with gas problems, there are more problems with digestive organs (listed above).
Bariatric surgery is as safe as gallbladder or appendix surgery in the hands of an expert and experienced doctor.
Bariatric surgery is a safe and effective treatment for obesity, but like any surgery, it does carry some risks and potential complications. Here are some of the common side effects and complications that can occur after bariatric surgery:
Complications during or after Bariatric Surgery, include:
- Complications related to Anaesthesia: Reactions to drugs used (anesthesia) or other medicines. Although rare, these can be serious because they can cause dangerously low blood pressures.
- Complications related to underlying medical illness like heart disease, diabetes, kidney disease, obesity, malnutrition.
- Complications related to Specific Operations, Bariatric Surgery:
- Infection of wound: 1-2%
- Bleeding: 0.1 – 1 %
- Blood clot in legs: 0.5-1%
- Vitamin deficiency: 10-30%
- Ulcer: 1-5%
- Weight Regain: 5-10%
- Conversion to open surgery: In a small number of patients the laparoscopic method is not feasible because of the inability to visualize or handle the organs (stomach or intestine) effectively. The decision to convert to an open procedure is strictly based on patient safety.
It’s important to remember that the risks and complications of bariatric surgery are relatively low, and the benefits of the procedure typically outweigh the risks.
Most patients experience significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related health problems after bariatric surgery.
Choosing the best bariatric surgeon for your weight loss surgery is an important decision. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a bariatric surgeon:
- Credentials: Look for a bariatric surgeon who is board-certified and has specialized training and experience in bariatric surgery. Check their credentials and certifications, and make sure they have a good track record of successful surgeries.
- Experience: Choose a bariatric surgeon who has performed a high volume of weight loss surgeries. Surgeons who perform a high volume of surgeries tend to have lower complication rates and better outcomes.
- Reputation: Look for a bariatric surgeon who has a good reputation in the medical community and among their patients. You can check online reviews, ask for referrals from other doctors, and talk to other patients who have had weight loss surgery.
- Communication: Choose a bariatric surgeon who communicates well with you and takes the time to answer your questions and address your concerns. You should feel comfortable talking to your surgeon and confident that they have your best interests at heart.
- Team: A bariatric surgeon is part of a larger team that includes nurses, dietitians, and other healthcare professionals. Look for a surgeon who works with a team that can provide comprehensive care before and after surgery.
- Cost: Weight loss surgery can be expensive, so it’s important to choose a surgeon who is transparent about their fees and who works with your insurance provider to maximize coverage.
Obesity is a long-standing disease that can have serious complications if left untreated. The longer the treatment is delayed, the greater the risk of developing these complications.
Here are some of the complications of obesity that can arise if treatment is delayed:
- Type 2 diabetes:
- Cardiovascular disease: Obesity increases the risk of developing heart disease and stroke (Paralysis).
- High Blood Pressure: Excess body fat can put a strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Sleep apnea: Obesity is a leading cause of sleep apnea, a condition in which a person’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- Joint problems: Obesity puts extra stress on the joints, particularly the knees and hips. Over time, this can lead to joint pain, osteoarthritis, and other joint problems.
- Mental health problems: Obesity can have a negative impact on mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
- Cancer: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of about 12 types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer.
- Reproductive health problems: Obesity can cause reproductive problems in both men and women. In women, obesity can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and complications during pregnancy. In men, obesity can lead to low testosterone levels, erectile dysfunction, and other reproductive problems.
The good news is that many of these complications can be prevented or managed through weight loss and other lifestyle changes. If you are struggling with obesity, it’s important to seek treatment as soon as possible to minimize your risk of developing these complications.
- Wound care: keep it dry and clean. Apply water proof bandage.
- Rest: Take Sufficient rest, but avoid over-resting
- Diet: Take a healthy & nutritious home-made diet.
- Activity: Walk regularly
- Bath: Take regular Bath
- Engage in reading & meditation
- Follow doctors’ advice
- Medicines: Take all medicines
