Reading Time: 4 minutes
BioFire Test Explained: A Complete Guide to Rapid Molecular Diagnosis in Modern Healthcare
What Is BioFire Test? Benefits, Panels & Cost Explained. What Is BioFire Test? Benefits, Panels & Cost Explained. Timely and accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective medical treatment. In infectious diseases, delays in identifying the exact pathogen can result in inappropriate antibiotic use, prolonged hospital stays, increased costs, and sometimes life-threatening complications. Traditional diagnostic methods like culture and microscopy, while valuable, often take hours to days and may fail to detect fastidious or viral organisms.
This diagnostic gap has been revolutionized by syndromic molecular testing, and one of the most widely adopted platforms in this category is the BioFire Test. Using multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, BioFire allows clinicians to identify multiple pathogens simultaneously from a single patient sample—often within an hour.
This article provides a comprehensive, clinician-friendly explanation of the BioFire Test, including how it works, available panels, clinical indications, advantages, limitations, and its growing role in evidence-based patient care.
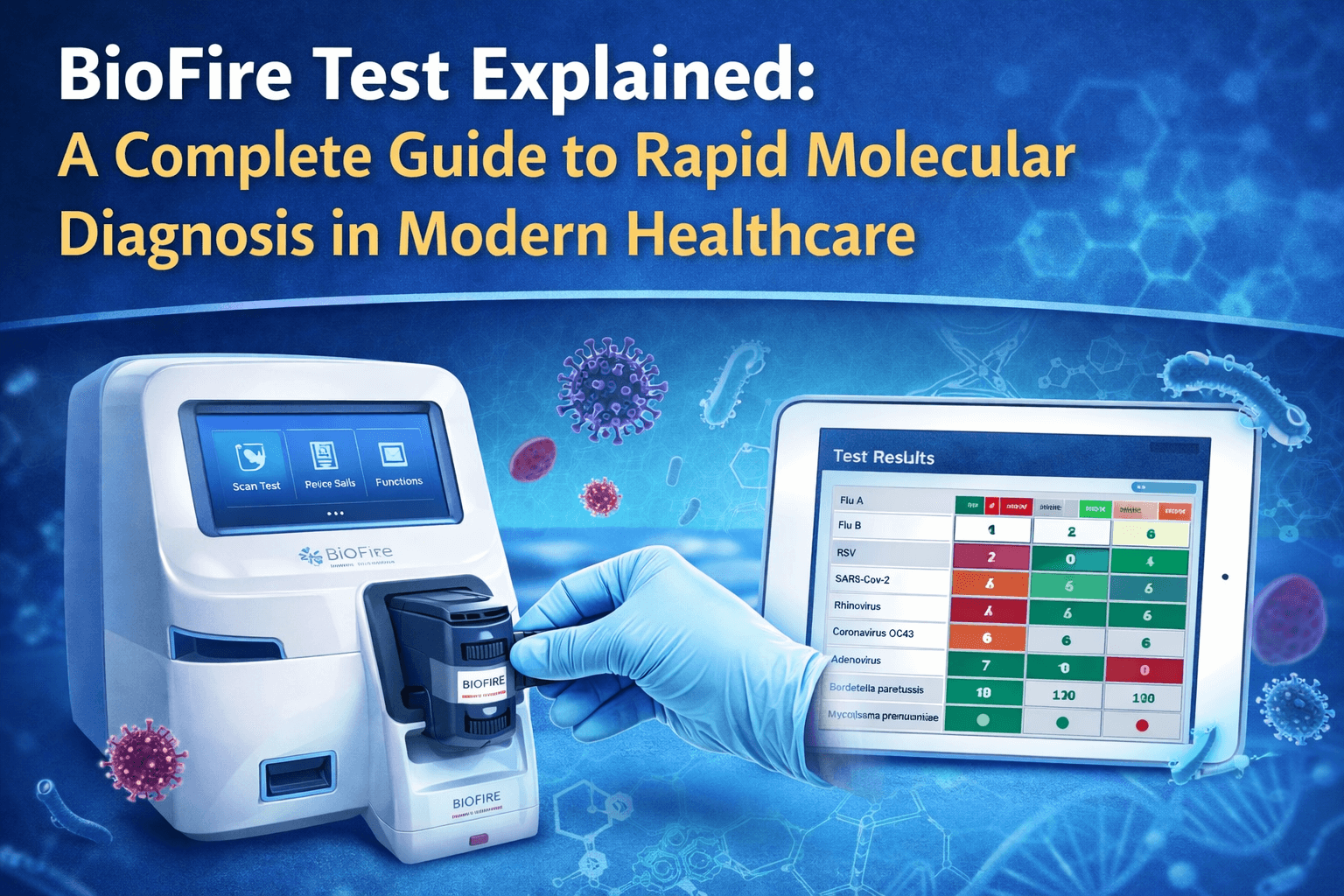
What Is the BioFire Test?
The BioFire Test is a fully automated multiplex PCR diagnostic system designed to detect multiple bacterial, viral, and parasitic pathogens at the same time from a single clinical specimen. It is performed using the FilmArray System, developed by bioMérieux, a global leader in in-vitro diagnostics.
Instead of testing for one organism at a time, the BioFire platform follows a syndromic approach—meaning it tests for all common causes of a specific clinical syndrome (such as diarrhea, respiratory infection, meningitis, or sepsis) in one run.
How Does the BioFire Test Work?
The BioFire Test integrates multiple molecular steps into a single, closed cartridge system, reducing contamination risk and operator dependency.
Step-by-Step Process
- Sample Collection
Depending on the panel, the sample may include:
- Stool
- Nasopharyngeal swab
- Blood culture bottle
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Loading the Pouch
The specimen is added to a disposable BioFire test pouch containing:
- Reagents
- Primers
- Internal controls
- Automated Processing
Inside the instrument:
- Nucleic acids are extracted
- Reverse transcription (for RNA viruses) occurs
- Nested multiplex PCR amplification is performed
- Detection & Interpretation
Results are generated automatically and displayed as Detected / Not Detected, typically within 45–90 minutes.
What Is Syndromic Testing?
Syndromic testing refers to testing based on clinical presentation rather than a suspected single pathogen.
For example:
- Acute diarrhea → Test for bacteria, viruses, parasites together
- Fever with altered sensorium → Test CSF for meningitis pathogens
- Flu-like symptoms → Test for influenza, RSV, COVID-19, adenovirus, etc.
This approach is especially valuable when:
- Symptoms overlap
- Co-infections are possible
- Rapid clinical decisions are required
Types of BioFire Panels
BioFire offers multiple FDA-approved and CE-marked panels, each designed for a specific clinical syndrome.
1. BioFire Gastrointestinal (GI) Panel
Sample: Stool
Turnaround Time: ~1 hour
Pathogens Detected: 22
Bacteria
- Salmonella
- Shigella / EIEC
- Campylobacter
- Vibrio species
- Clostridioides difficile (toxin genes)
- Diarrheagenic E. coli (EPEC, ETEC, EAEC, STEC)
Viruses
- Norovirus
- Rotavirus
- Adenovirus
- Astrovirus
- Sapovirus
Parasites
- Giardia lamblia
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Cryptosporidium
Clinical Use:
- Acute infectious diarrhea
- Hospital-acquired diarrhea
- Diarrhea in elderly, ICU, or cirrhotic patients
- Post-antibiotic diarrhea
2. BioFire Respiratory Panel
Sample: Nasopharyngeal swab
Pathogens: Up to 20+
Detects:
- Influenza A/B
- RSV
- SARS-CoV-2
- Adenovirus
- Parainfluenza
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydia pneumoniae
Clinical Use:
- Influenza-like illness
- Pneumonia
- COVID-19 differential diagnosis
- Pediatric respiratory infections
3. BioFire Blood Culture Identification (BCID) Panel
Sample: Positive blood culture
Detects:
- Gram-positive bacteria
- Gram-negative bacteria
- Yeast
- Antimicrobial resistance genes (e.g., mecA, vanA, KPC)
Clinical Use:
- Sepsis
- Septic shock
- ICU bloodstream infections
4. BioFire Meningitis/Encephalitis Panel
Sample: CSF
Detects: 14 pathogens including:
- HSV-1, HSV-2
- VZV
- Enterovirus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Neisseria meningitidis
- Cryptococcus neoformans
Clinical Use:
- Acute meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Febrile seizures with CNS symptoms
Advantages of the BioFire Test
1. Rapid Turnaround Time
Results in less than 1 hour, compared to:
- Culture: 24–72 hours
- Microscopy: Variable sensitivity
2. Broad Pathogen Coverage
Simultaneous detection of bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
3. High Sensitivity & Specificity
PCR-based detection allows identification even when:
- Pathogen load is low
- Antibiotics have already been started
4. Improved Antibiotic Stewardship
- Early identification of viral infections
- Reduction in unnecessary antibiotics
- Targeted antimicrobial therapy
5. Detection of Co-Infections
Identifies multiple pathogens in the same sample.
6. Minimal Operator Dependency
Closed system reduces contamination and technical errors.
Limitations of the BioFire Test
Despite its strengths, BioFire is not without limitations.
1. Cost
- More expensive than routine stool or culture tests
- Best used selectively in high-risk patients
2. Detection of DNA, Not Viability
- Detects genetic material, not live organisms
- Colonization vs infection must be clinically correlated
3. Limited Antimicrobial Susceptibility
- Resistance genes detected, but full sensitivity testing still requires culture
4. Not a Replacement for Clinical Judgment
Results must be interpreted in clinical context.
BioFire vs Conventional Diagnostic Tests
| Feature | BioFire Test | Conventional Culture |
| Turnaround Time | ~1 hour | 1–3 days |
| Pathogens | Multiple | Single |
| Sensitivity | High | Variable |
| Antibiotic Guidance | Early | Delayed |
| Labor | Minimal | High |
Clinical Scenarios Where BioFire Is Most Useful
- Severe acute diarrhea with dehydration
- Diarrhea in cirrhosis or immunocompromised patients
- ICU sepsis of unknown origin
- Pediatric meningitis
- Respiratory outbreaks
- Hospital infection control surveillance
Role of BioFire in Infection Control & Public Health
- Early outbreak detection
- Rapid isolation decisions
- Reduced hospital transmission
- Data-driven antimicrobial policies
Is BioFire Test Available in India?
Yes. BioFire systems are increasingly available in:
- Tertiary care hospitals
- Corporate hospital chains
- Advanced diagnostic laboratories
Availability may vary by city and institution, and test cost depends on the panel used.
Cost of BioFire Test (Approximate)
| Panel | Estimated Cost (INR) |
| GI Panel | ₹6,000 – ₹10,000 |
| Respiratory Panel | ₹4,000 – ₹7,000 |
| BCID Panel | ₹5,000 – ₹9,000 |
| ME Panel | ₹7,000 – ₹12,000 |
(Prices vary by hospital and region)
Future of BioFire and Syndromic Molecular Testing
With increasing antimicrobial resistance and emerging infections, syndromic molecular diagnostics represent the future of infectious disease management. BioFire continues to evolve with:
- Expanded panels
- Faster turnaround
- Integration with hospital information systems
- AI-driven data interpretation
Conclusion
What Is BioFire Test? Benefits, Panels & Cost Explained. The BioFire Test represents a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostics, moving from slow, organism-by-organism testing to rapid, syndrome-based molecular diagnosis. When used judiciously, it improves patient outcomes, reduces hospital stays, supports antibiotic stewardship, and enhances infection control.
For hospitals, clinicians, and patients alike, BioFire is not just a test—it is a powerful clinical decision-making tool in modern medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is BioFire better than stool culture?
Yes, in acute and severe cases where rapid diagnosis is essential.
Can BioFire detect parasites?
Yes, the GI panel detects common protozoal parasites.
Does a positive BioFire result always mean infection?
Not always. Clinical correlation is essential.
Is BioFire safe?
Yes. It is a closed, automated system with minimal contamination risk.
